5Minute Brain MRI Can Reveal Risk for Alzheimer's Disease
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a large magnet, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body. In this case, the images are of the brain and spine. MRI is used to help diagnose a health problem. The MRI machine is a large, tube-shaped machine that creates a strong magnetic field around.
MRI scan image of brain Regional Medical Imaging
MRI is firmly established as an essential modality in the imaging of the temporal bone and lateral skull base. It is used to evaluate normal anatomic structures, evaluate for vestibular schwannomas, assess for inflammatory and/or infectious processes, and detect residual and/or recurrent cholesteatoma. It is also extensively used in pre- and postoperative evaluations, particularly in patients.
resonance image (MRI) of the brain ODC

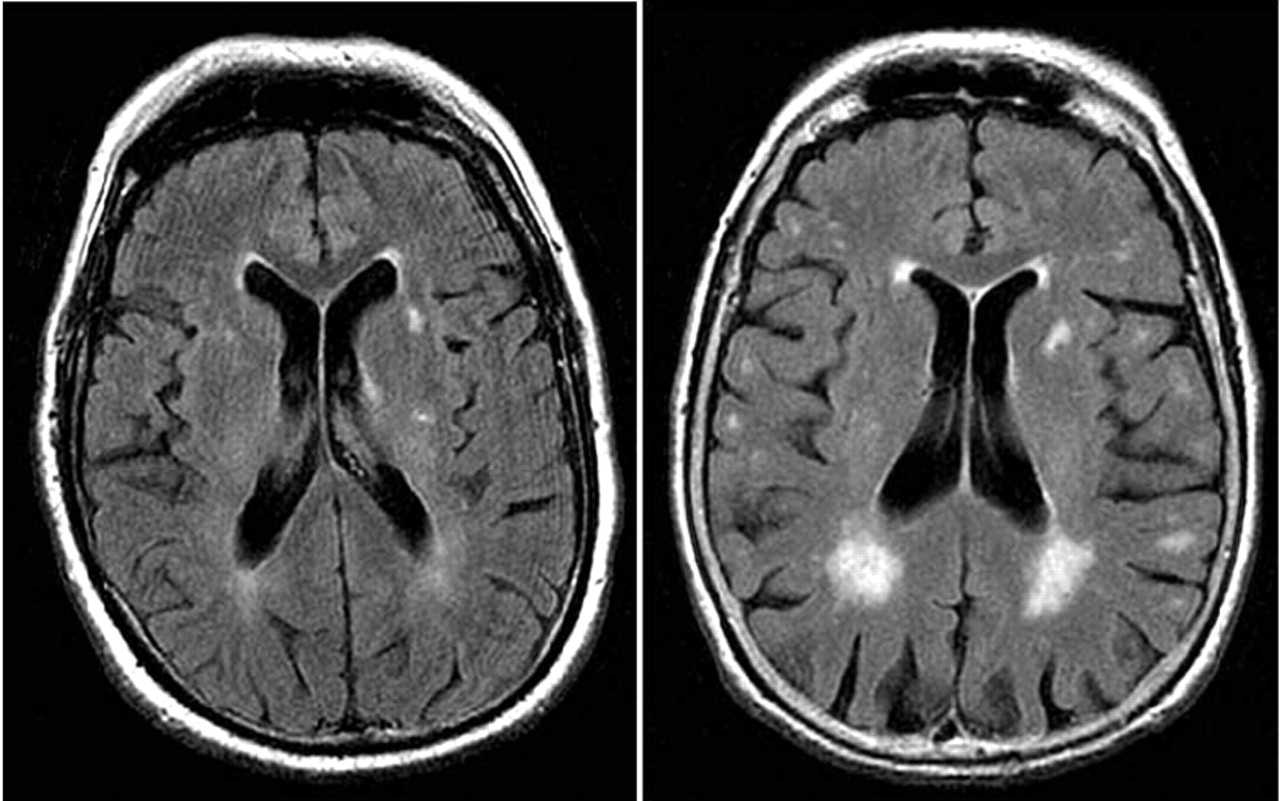
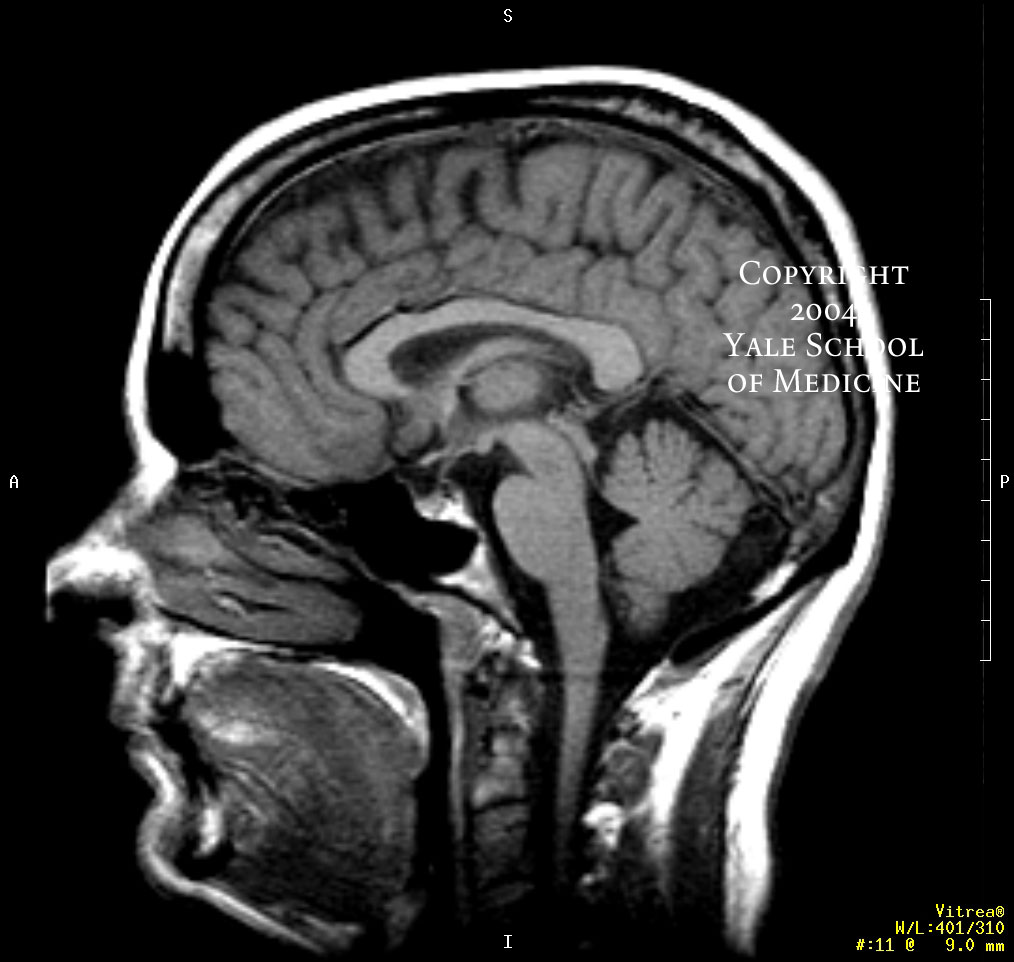
Normal brain MRI. A brain MRI is one of the most commonly performed techniques of medical imaging. It enables clinicians to focus on various parts of the brain and examine their anatomy and pathology, using different MRI sequences, such as T1w, T2w, or FLAIR. MRI is used to analyze the anatomy of the brain and to identify some pathological.
CT Scans vs. MRIs Differences, Benefits, and Risks Mri scan, Ct scan, Mri

A brain MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan, also called a head MRI, is a painless procedure that produces very clear images of the structures inside of your head — mainly, your brain. MRI uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer to produce these detailed images. It doesn't use radiation. Currently, MRI is the most sensitive.
CT vs. MRI What's the Difference? Windom Area Health
A brain MRI, also called a head MRI, uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce pictures of the brain. The pictures produced are clearer and more detailed than other imaging methods. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) does not use ionizing radiation and may require an injection of a contrast material called gadolinium.
Brain MRI scan protocols, positioning and planning YouTube

Functional MRI (fMRI) shows which brain regions are activated (shown by increased flow of oxygenated blood) by a specific cognitive or motor task, but its clinical use is still being defined. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) uses MRI with or without a contrast agent to show cerebral vessels and major arteries and their branches in the head.
Mri Abnormal Brain Scan
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of a large magnet, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body. Unlike X-rays or computed tomography (CT scans), MRI does not use ionizing radiation. Some MRI machines look like narrow tunnels, while others.
Brain Mri Scan Machine
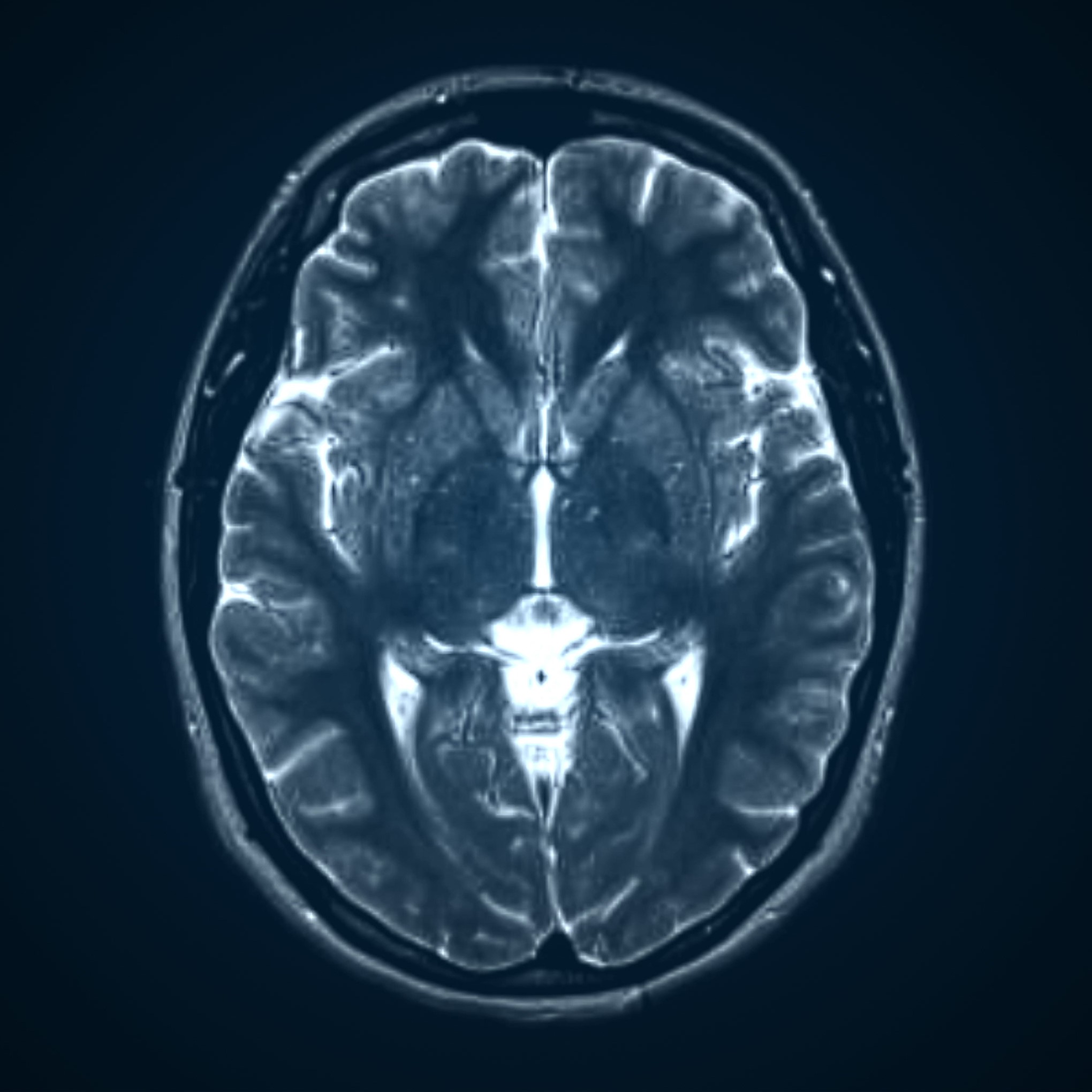
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The internal acoustic canal (IAC) , also known as the internal auditory canal or meatus (IAM), is a bony canal within the petrous portion of the temporal bone that transmits nerves and vessels from within the posterior cranial fossa to the auditory and vestibular apparatus.
Normal brain MRI Radiology Case Brain images, Mri, Brain scan

Acquired audiovestibular symptoms may be an indicator of cerebellopontine angle (CPA), internal auditory meatus (IAM) or inner ear disorders, such as meningioma, vestibular schwannoma (VS), cholesterol granuloma or fibrosis of the labyrinth. Such pathologies may be accurately diagnosed with MRI. Hearing loss (asymmetric or unilateral) as a clinical symptom or as demonstrated on pure tone.
Cureus GuillainBarre Syndrome, Neuroborreliosis, or Both
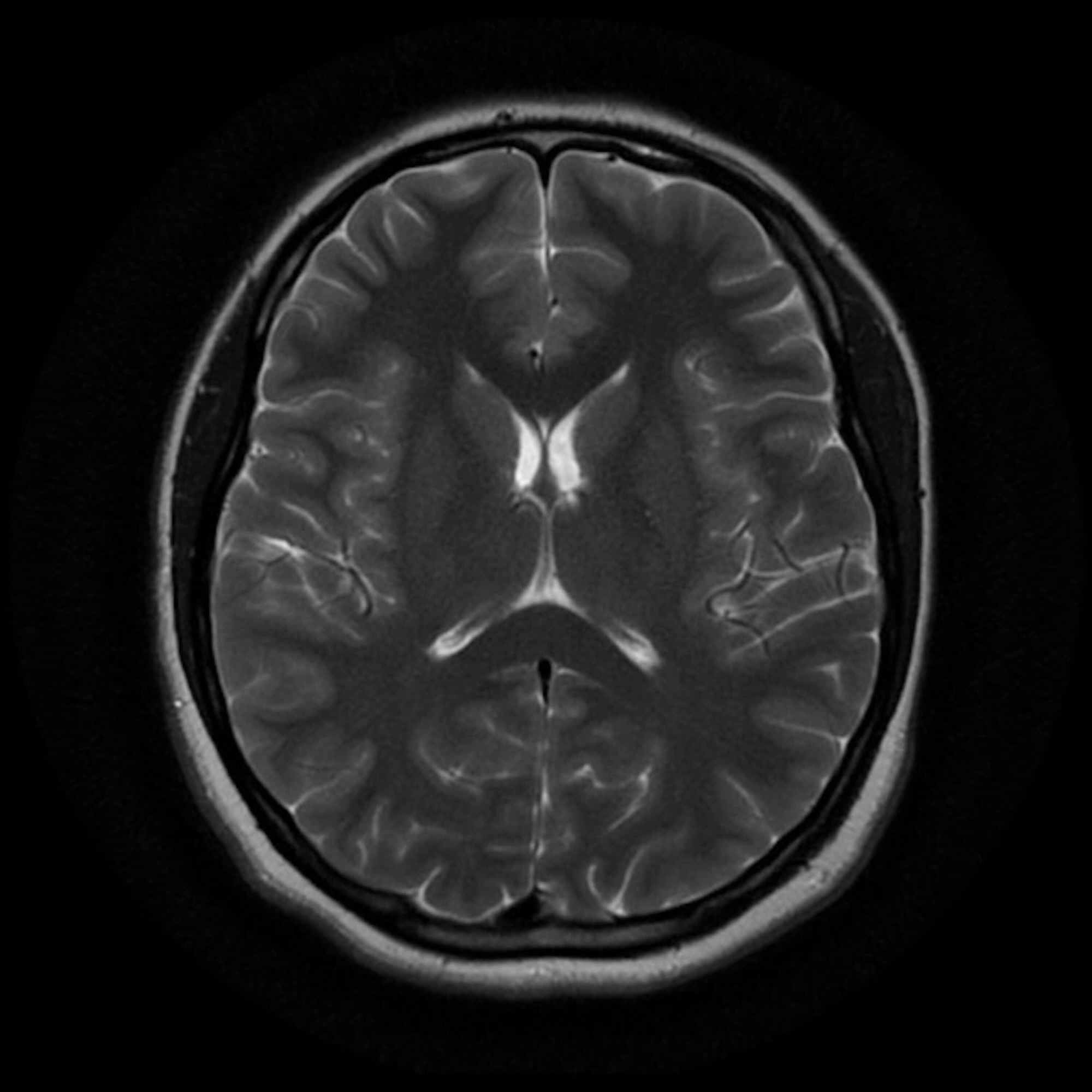
an additional exam that may help assess the finding (such as a CT or PET exam of the brain). a follow-up brain MRI to see if the finding changes over time. a follow-up brain MRI with contrast to see if the finding enhances. a biopsy. that your doctor correlates the imaging finding with clinical symptoms or laboratory test results.
Top 18 what is an mri scan used to diagnose 2022
T2 TSE coronal 3mm. Plan the coronal slices on the axial plane and angle the planning block parallel to the line along the right and left Internal Auditory Meatus (IAMS) (as shown in the diagram). Verify the planning block in the other two planes. Ensure an appropriate angle is maintained in the sagittal plane, parallel to the brain stem.
My Brain MRI Scan Result Images YouTube
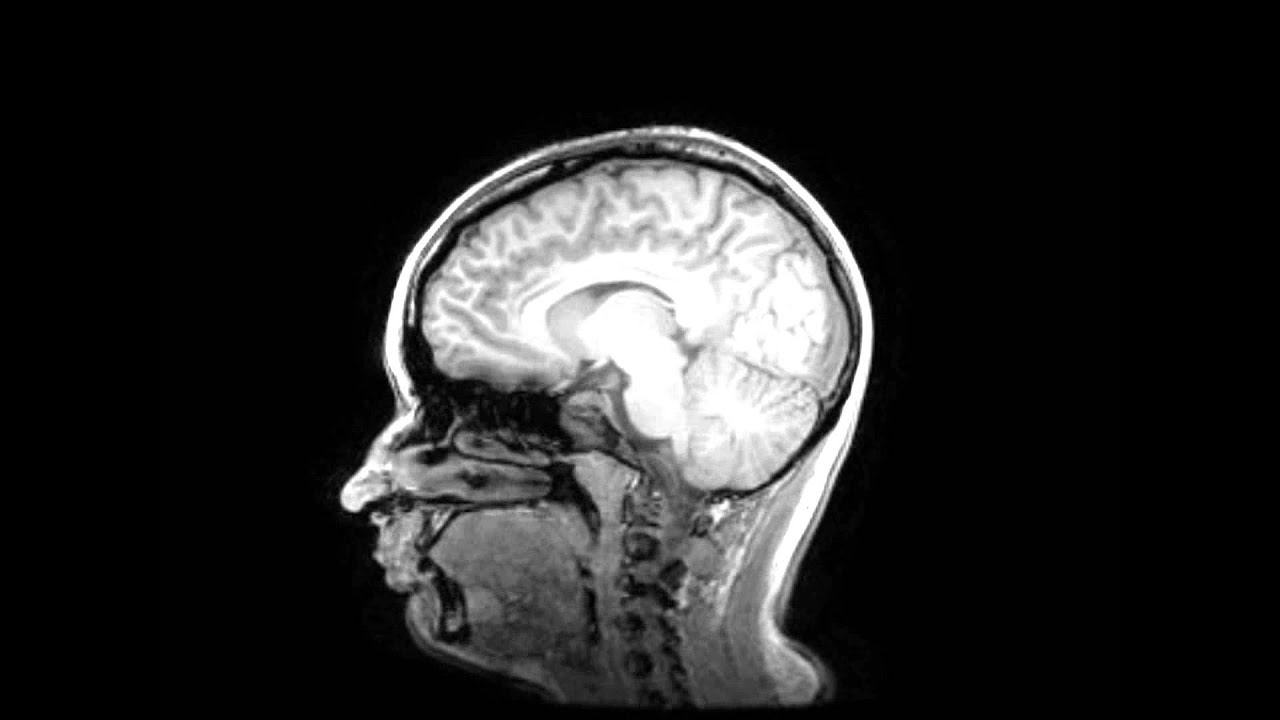
An MRI IAM will look at the nerves responsible for hearing and balance. It also shows the fluid in the inner ear (membranous labyrinth). We also get some limited images of the brain. We can pick up certain abnormalities of the hearing pathway, including: Benign tumours (acoustic neuroma, also known as vestibular schwannoma) Problems with the.
Recurrent vertigo associated with headaches The BMJ

Investigation of these patients includes thorough clinical examination, audiological evaluation and frequently Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Internal Auditory Meatus (IAM), cerebellopontine angle (CPA) and brain. MRI scanning is a well-established, cost-effective investigation for these patients [1-3]. Only a small percentage of these.
MRI Scans What to Expect at Moffitt Cancer Center YouTube

Investigation of these patients includes thorough clinical examination, audiological evaluation and frequently Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Internal Auditory Meatus (IAM), cerebellopontine angle (CPA) and brain. MRI scanning is a well-established, cost-effective investigation for these patients [1-3]. Only a small percentage of.
22C+ October 2010
Normal MRI IAM for reference. T2 SPACE ISO is a sequence used for high-resolution images, especially to visualise the facial and vestibulocochlear nerves in the cerebellopontine angle region. T2 SPACE ISO is specific for Siemens MRI machines. Other names include CUBE (for GE), VISTA (for Philips), isoFSE (for Hitachi), and 3D MVOX (for Canon).
MRI Reveals Striking Brain Differences in People With Autism Brain scan, Mri brain

MRI is also a tomographic imaging modality, in that it produces two-dimensional images that consist of individual slices of the brain. Images in MRI need not be acquired transaxially, and the table or scanner does not move to cover different slices in the brain. Rather, images can be obtained in any plane through the head by electronically.